Google Analytics 4 has been hyped for its customer-centric measurement abilities, no longer fragmented by device or platform. But you can’t get to this point in GA4 without some customization. Today we’ll explore how you can configure GA4 for maximum user journey reporting.

What is Reporting Identity in Google Analytics 4?
The “Reporting Identity” in GA4 refers to the method you would like to use to identify a user. There are three IDs that GA4 might use:
The Device ID
On the web, this is known as the client ID. It is a random integer stored in a first-party cookie on the user’s first visit and set to persist for 2 years. In the classic version of Google Analytics (pre-2013) this was the only option. In a mobile app, this is set to the App-Instance ID.
The User ID
This was released with Universal Analytics and allows you to set a value that Google should use to recognize a user when a user is authenticated. With the user ID, companies were able to view a logged-in user’s activity across mobile and desktop devices for the first time.
Google Signals
This is the new option that uses the Google account, and it is only available for users who have enabled Ads Personalization.
When you create a property in Google Analytics 4, you can set the Reporting Identity from the property settings menu. The selection you make here will apply to all of your reports in GA4.
User Identification Options
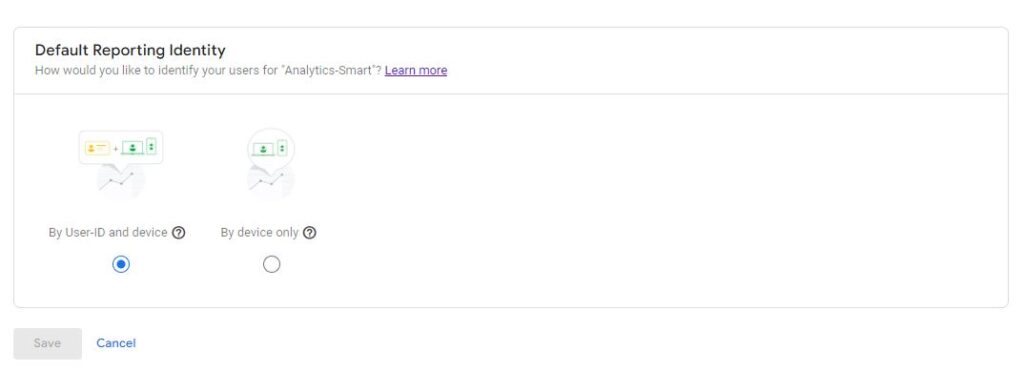
Default Reporting Identity
Having both User-ID and Google Signals enabled provides the most accurate user reporting. If you do not have Signals enabled, Google defaults to “By User-ID and device.” You can choose to rely on “By device only” although this will give you comparable user reporting to Universal Analytics.
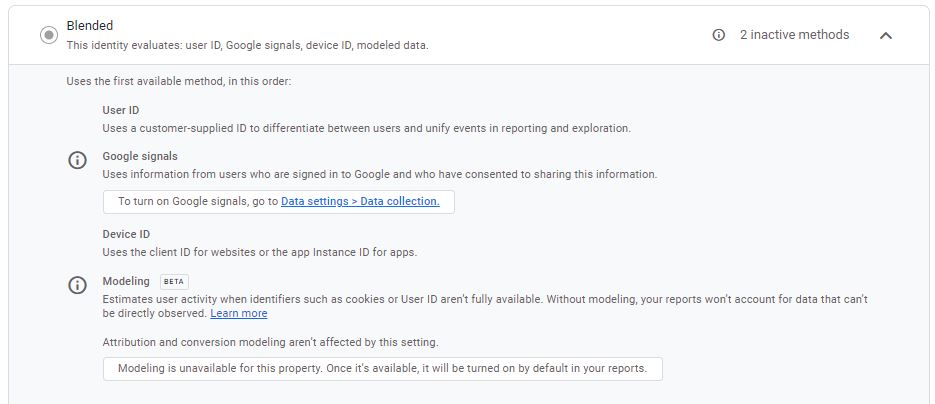
Blended Reporting Identity
Behavioral modeling for consent mode aims at filling this data gap by modeling the behavior of users who decline analytics cookies based on the behavior of similar users who accept analytics cookies. The training data used for modeling is based on the consented user data from the property where modeling is activated
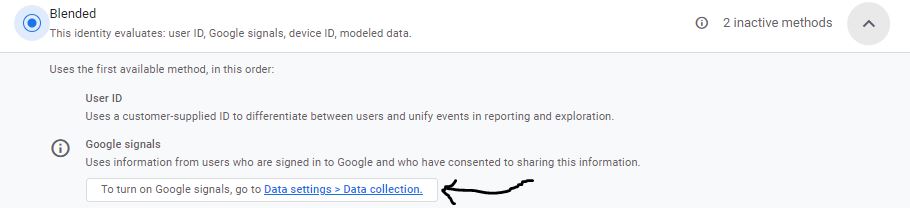
Step 1:
Click on Data settings–> Data collection link
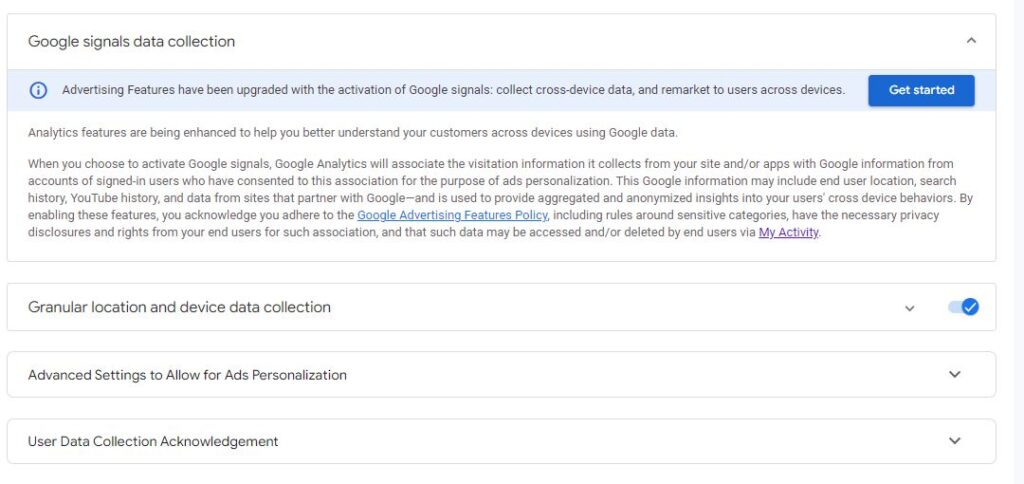
Step 2:
Enable Google Signal Data collection- Advertising Features have been upgraded with the activation of Google signals: collect cross-device data, and remarket to users across devices.
Step 3:
Click on activate Google Signals
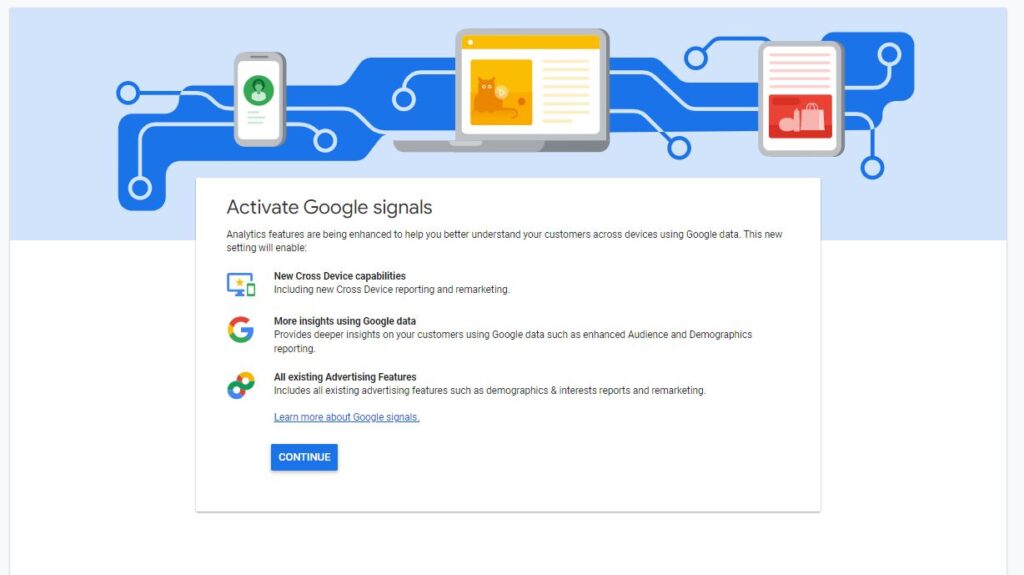
Step 4:
Analytics features are being enhanced to help you better understand your customers across devices using Google’s signed-in data. This new setting will enable:
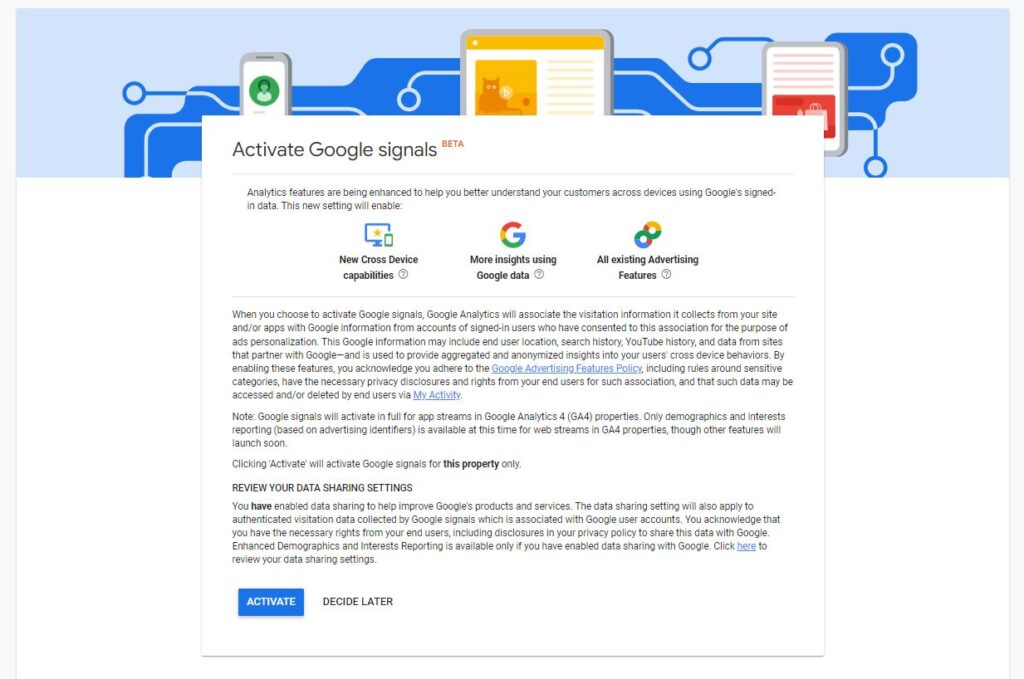
Step 5:
Acknowledgment of services
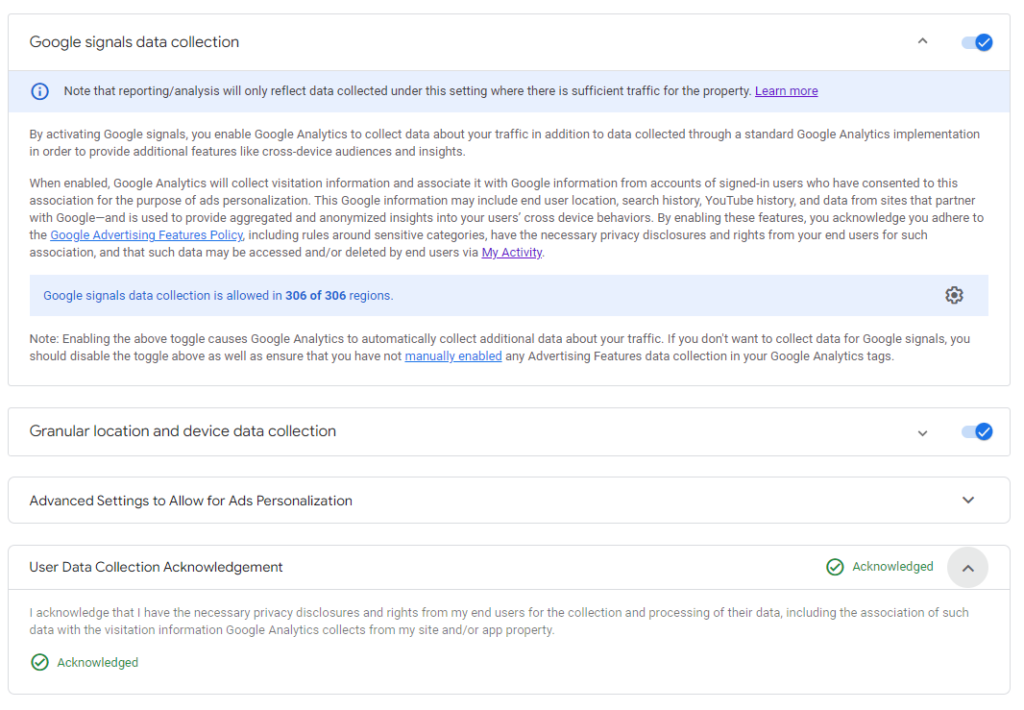
Observed Reporting Identity
When you select this option, you are telling GA4 to use the best identifier available. If your user has authenticated and a user ID exists, then this method will be used because it is the most accurate. Otherwise, if Google signals data is available, this method will be used. Finally, if there is no other option, the last resort will be the device ID (again, this is the client ID for the web).
NOTE: You can find Google’s documentation on reporting identity HERE.
At this point, you’re probably wondering why anyone would choose “By device only.” The answer is privacy, so let’s discuss that next.
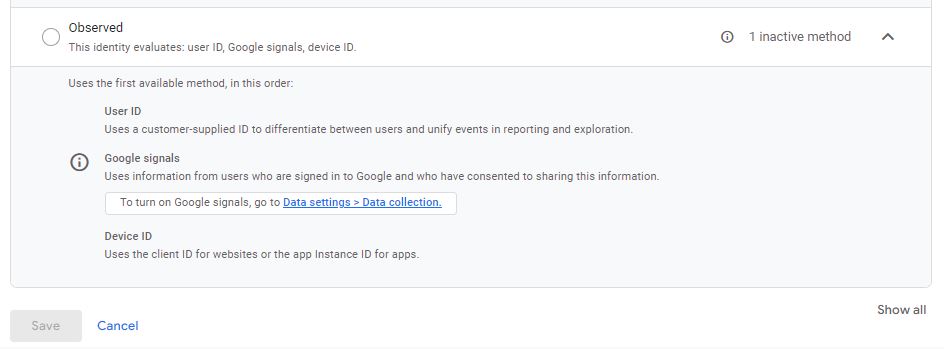
Modeled data vs. observed data
When users visit your site and grant consent for Analytics cookies or when they don’t opt-out of personalization using advertising ID in Android Settings, Analytics associates user behavior with various identifiers to provide continuity in measurement. Google refers to this kind of data as observable data because it comes from users who have given us permission to observe their behavior.
When users don’t grant consent to the use of Analytics cookies or equivalent app identifiers, events are not associated with a persistent user identifier. For example, if Analytics collects 10 pageview events, it can’t observe and report whether that’s 10 users or 1 user. Instead, Analytics applies machine learning to estimate the behavior of those users based on the behavior of similar users who do accept analytics cookies or equivalent app identifiers.
Conclusion
So, this confirms that Google Analytics 4 introduces smart analytics features to capture end-user behavior based on Machine Learning.






2 Comments
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thank you very much for sharing, I learned a lot from your article. Very cool. Thanks.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thank you very much for sharing, I learned a lot from your article. Very cool. Thanks.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://accounts.binance.info/sl/register?ref=IJFGOAID
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.com/zh-CN/join?ref=VDVEQ78S
[…] Identity Spaces Available in Google […]
[…] This is the biggest concern with this minimal setup in Google Tag Manager, Google is continuing to collect data when the visitor has explicitly mentioned not to track. The same is also explained in the official documentation. The idea is to collect “anonymized” data from non-consenting visitors so that they can create a behavioral model in Google Analytics. As I have shared the same in my Reporting Identity Post […]